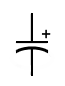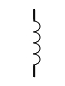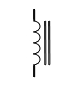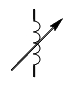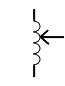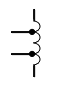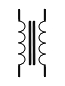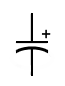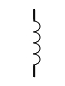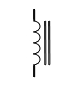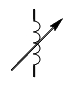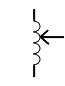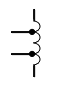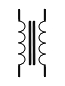| Name |
Symbol |
Notes |
| Resistors |
| Resistor |
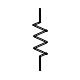 |
Resists current flow |
| Resistor, tapped |
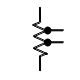 |
A fixed resistor having one or more additional terminals along its length, generally for voltage-divider applications |
| Resistor, variable (potentiometer) |
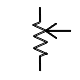 |
Three terminals; usually used to control voltage |
| Resistor, variable (rheostat) |
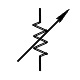 |
Two terminals; usually used to control current |
| Photoresistor |
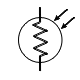 |
Converts light to resistance |
| Thermistor |
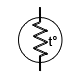 |
Thermal resistor; resistance varies significantly with temperature |
| Capacitors |
| Capacitor, non-polar |
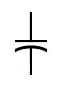 |
Stores electric charge; acts as short circuit with AC and open circuit with DC |
| Capacitor, polar |
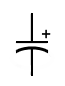 |
Only operates properly when connected to proper polarity (one lead is positive, the other negative) |
| Capacitor, variable |
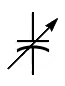 |
Capacitance may be varied mechanically or electronically |
| Inductors |
| Inductor |
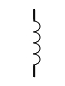 |
Generates magnetic field |
| Inductor, iron core |
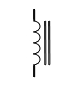 |
Uses a ferromagnetic core to increase inductance |
| Inductor, variable |
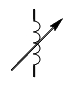 |
Provides varying output voltage |
| Inductor, variac |
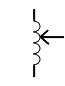 |
Variable autotransformer providing a continuously adjustable output voltage |
| Inductor, tapped |
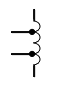 |
Taps allow for different voltage outputs |
| Diodes |
| Diode |
 |
Allows current flow in one direction only (in direction of arrow) |
| Light emitting diode (LED) |
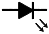 |
Emits light when current flows through |
| Photodiode |
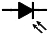 |
Allows current flow when exposed to light |
| Tunnel diode |
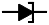 |
Has a negative resistance at very low voltage |
| Varactor |
 |
Used as a voltage-controlled capacitor |
| Zener diode |
 |
Allows current flow in one direction, but also can flow in the reverse direction when above breakdown voltage |
| Transistors |
| Transistor, NPN |
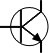 |
Allows current flow when the collector voltage is larger than the emitter voltage |
| Transistor, PNP |
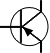 |
Allows current flow when the emitter voltage is larger than the collector voltage |
| Phototransistor |
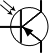 |
Allows current flow when exposed to light |
| Switches |
| Pushbutton, normally open |
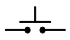 |
Allows current to flow only when pressed |
| Pushbutton, normally closed |
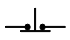 |
Open (off) only when pressed |
| Single-pole, single-throw (SPST), normally open |
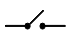 |
Simple on-off switch |
| Single-pole, single-throw (SPST), normally closed |
 |
Open (off) only when switched |
| Single-pole, double-throw (SPDT) |
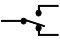 |
A changeover switch; has two "on" positions and one "off" position |
| Double-pole, single-throw (DPST) |
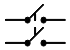 |
A dual on-off switch; simultaneously opens or closes two separate circuits or both sides of the same circuit |
| Double-pole, double-throw (DPDT) |
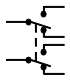 |
Consists of two separate switches that operate at the same time, with one normally open and one normally closed |
| Electron Tubes |
| Diode |
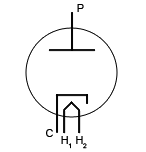 |
Two electrodes--cathode (C) and plate (P) (the plate is also known as the anode (A)); the heater (H) is used to stimulate electron flow |
| Glow tube |
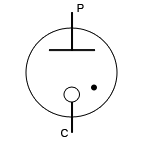 |
Diode used for voltage regulation |
| Phototube |
 |
Diode that is sensitive to light; current flow is dependent on intensity and frequency of incoming photons |
| Triode |
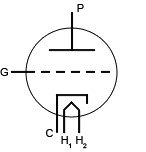 |
Three electrodes--cathode (C), plate (P), and grid (G) |
| Tetrode |
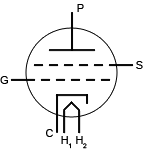 |
Four electrodes--cathode (C), plate (P), grid (G), and screen (S) |
| Beam tetrode |
 |
Beam-forming electrodes allow more power output than a similar pentode |
| Pentode |
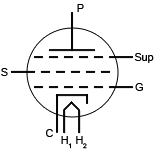 |
Five electrodes--cathode (C), plate (P), grid (G), screen (S), and suppressor (Sup) |
| Miscellaneous |
| AC power supply |
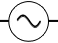 |
Provides AC power |
| Antenna |
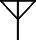 |
Transmits/receives radio waves |
| Antenna, dipole |
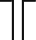 |
Two-wire antenna |
| Amplifier |
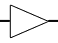 |
Increases input signal |
| Battery |
 |
Provides DC power |
| Cell |
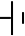 |
Batteries contain one or more cells |
| DC power supply |
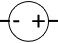 |
Provides DC power |
| Fuse |
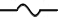 |
Opens when subjected to current above stated threshold |
| Generator |
 |
Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy |
| Ground, earth |
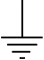 |
Provides electrical shock protection |
| Ground, chassis |
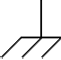 |
Connected to circuit chassis |
| Ground, signal (common) |
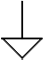 |
Reference point for all signals in a circuit; commonly, the same as the circuit ground |
| Headphones |
 |
Converts electrical signals to sound waves |
| Lamp |
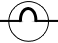 |
Used for indicating or lighting |
| Loudspeaker |
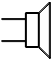 |
Converts electrical signals to sound waves |
| Meter |
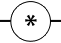 |
*A - ammeterDB - decibel meterF - frequency meterG - galvanometerMA - milliammeterΩ - ohmmeterV - voltmeterW - wattmeter |
| Microphone |
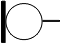 |
Converts sound waves to electrical signals |
| Motor |
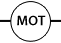 |
Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy |
| Piezoelectric crystal |
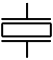 |
Converts electrical energy to sound waves |
| Relay |
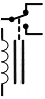 |
Opens and closes connections with an electromagnet |
| Transformer |
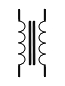 |
Changes AC voltage from high to low (step-down) or low to high (step-up) |
| Wire |
 |
Electrical current conductor |
| Wires, joined |
 |
Connected crossing wires |
| Wires, not joined |
 |
Unconnected crossing wires |